3-D Printing Is Revolutionizing Dentistry
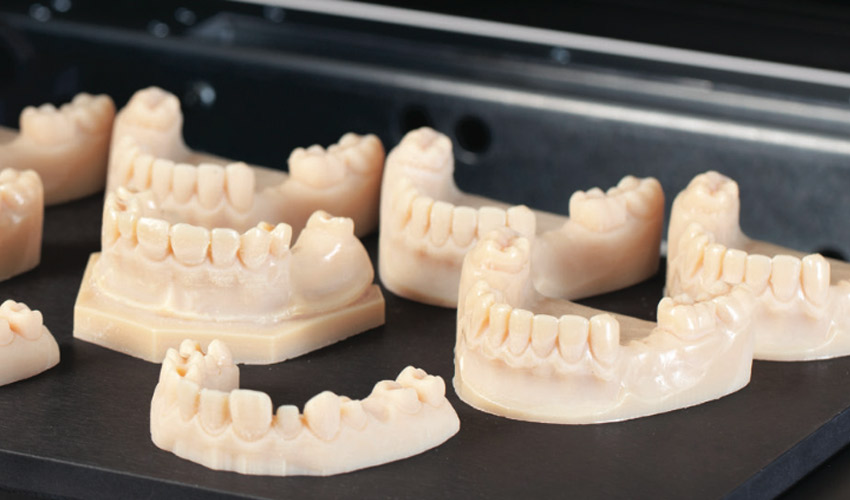
As a manufacturing technique borne out of the ’80s, 3-D printing has only become more relevant now due to the advent of prototyping in lean methodologies. It has greatly revolutionized the industry in so many ways, particularly digital dentistry. The use of 3-D printing in dentistry has developed as a necessity due to precision science. Offering more precise digital models to the manufacture of orthodontic products makes the whole process lean and fast.
Key Technologies in Dental 3-D Printing
Additive manufacturing in dentistry involves a number of technologies. Each type works on specific applications and uses. The most common technologies are fused deposition modeling (FDM), photopolymerization, metal additive manufacturing, and selective laser sintering (SLS).
Fused Deposition Modeling
This is a process that produces manufactures at a very low cost, but no post-processing is involved after printing. An object, following a computer-aided design model, is created through layer-by-layer deposition of plastic filaments using a nozzle. Normally, it is used to manufacture orthodontic models mainly for thermoform gutters. Purposes include alignment, bleaching, and restraint.
Photopolymerization
This is the most used additive process in dentistry. It uses light, allowing polymerization reaction to create a polymer structure or material. This structure can be either linear or cross-linked. It provides a significantly higher resolution, ensuring more accurate devices to be printed. Materials are also biocompatible. Compared to other techniques, photopolymerization goes for precision better.
Metal Additive Manufacturing
This is a process that builds a 3-D object using a digital file. This process is used to create implants, screeds, and stellites. A highly capital intensive process, it is indeed more expensive to acquire and use. There is post-processing work included, eroding some productivity in the process. But results are more valuable as this technique can create complex shapes that traditional or subtractive methods cannot produce.
Selective Laser Sintering
This is an additive manufacturing technology that utilizes lasers to sinter a material into a solid, whole structure. This process is cheap per product made and is very productive. It is also versatile and workable in many applications, from functional prototyping to bridge manufacturing. The most common SLS systems are plastic-based (selective laser melting) and metal-based (direct metal laser sintering) systems.
Rapid Growth for the Next Decade
3-D printing is an efficiency machine. It is estimated that dental 3-D printing will grow even further, reaching a market value worth $9.5 billion in 2027. Considering the surge in the use of the manufacturing technique, the market has reported a high return on investments as well as improved work productivity.
Analysts have also attributed the growth to third-party manufacturers. These manufacturers make the resins. With the high demand for 3-D printed orthodontic materials and products, these manufacturers will only respond by supplying more resins to the market.
Dental 3-D printing is sure to benefit from the many technologies or processes available in additive manufacturing. The adoption of such technologies has been swift and is expected to expand. This is so as more demand for 3-D printed orthodontic products is making dentistry a lucrative market for precision methods. Find out more about orthodontic procedures when you get your crown fitted in El cajon.