How Is Ovarian Cancer Diagnosed?
A variety of tumors can cause ovarian cancers. Out of these, high-grade serous carcinoma is the most common type of tumor and is responsible for 70% of ovarian cancer cases.
Women who use talc products such as Johnson & Johnson’s baby powder, Valeant Pharmaceuticals’ shower to shower, etc. for personal hygiene have a 30% higher chance of getting ovarian cancer.
There are thousands of Talcum powder lawsuits filed that claim that the manufacturers of such talc products failed to warn the users against the health risks. Media articles have indicated alarming risk of Talcum powder cancer to the consumers.
Ovarian Cancer – Diagnosis
Treatment for ovarian cancer works the best when it is diagnosed in early stages. But it is difficult to detect early symptoms of ovarian cancer.
The ovaries are located deep within the abdominal cavity, and there is no usual diagnostic screening available for detecting ovarian cancer. If you are having any unusual or persistent symptoms, you need to consult your doctor for a pelvic exam.
Performing a rectovaginal pelvic exam helps the doctor to identify any irregularities. In this test, the doctor examines your ovaries, pelvis, rectum, uterus, cervix, vagina, and vulva for any abnormalities.
Other than rectovaginal pelvic examination, the doctor may also perform the following tests:
Biopsy
A biopsy involves removing a small specimen of affected tissue from the ovary during a laparoscopy procedure. The doctor can verify whether you have ovarian cancer or not by analyzing the sample under a microscope.
Blood Test
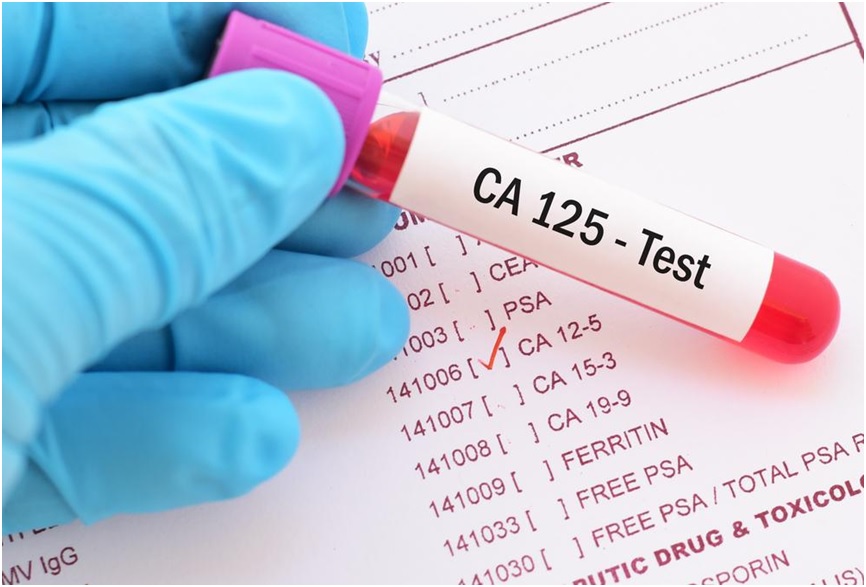
A blood test is done to measure the level of cancer antigen 125 (CA-125). It is used to evaluate the possible treatment response for ovarian cancer. However, uterine cancer, uterine fibroids, menstruation, and other reproductive organ cancers can also affect levels of CA-125 in the blood.
CT Scan
CT scan is an imaging method used to examine the abdominal and pelvic area. It creates cross-sectional pictures of the pelvis including prostate, bladder, lymph nodes, male and female reproductive organs etc.
Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS)
Transvaginal ultrasound is used to detect tumors in the reproductive organs. In this imaging test, the doctor uses sound waves to determine whether tumors are cancerous.
What Are The Different Stages Of Ovarian Cancer?
Depending on the severity of cancer, the stages are based on how far cancer has spread. Ovarian cancer has 4 stages, each of then has further sub-stages:
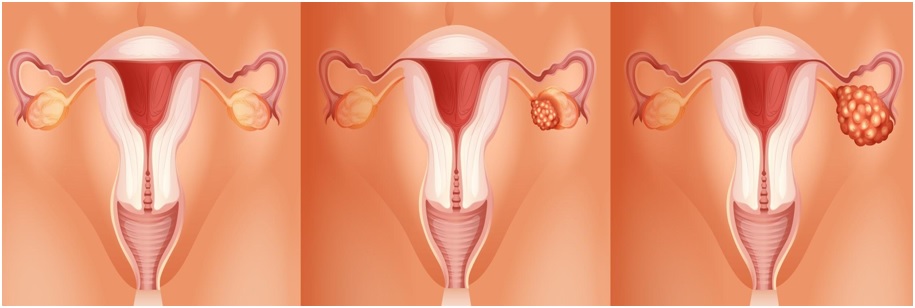
Stage 1
It has 3 sub-stages:
1A: The cancer is localized or limited to one ovary.
1B: The cancer is present in both ovaries.
1C: The cancer cell is present on the outside of the ovary.
Stage 2
It has two sub-stages where cancer starts spreading to other pelvic structures.
2A: cancer starts spreading to the fallopian tubes or uterus.
2B: cancer starts spreading to the rectum or bladder.
Stage 3
It has three sub-stages:
3A: The lymph nodes and the lining of the abdomen are affected by cancer
3B: The cancer cells are present outside of the liver or spleen.
3C: Visible cancer cells (at least 3/4 of an inch) are seen outside the spleen or liver or on the abdomen.
Stage 4
There are two sub-stages in stage 4 where the tumor has spread, beyond the lymph nodes, abdomen, and pelvis to the lungs or liver.
4A: The cancer cells are present in the form of fluid around the lungs.
4B: It is the most advanced stage where the cancer cells reached the inside of the liver or spleen or the other distant organs including brain and skin.
Treatment
The treatment of ovarian cancer depends on its stage. It involves a combination of surgery, radiation, therapy, and chemotherapy.
Conclusion
Choosing the right treatment may be hard for you. Consult your doctor to find out the latest possible treatment options available for your stage of ovarian cancer.