3D Printing Innovations and Techniques
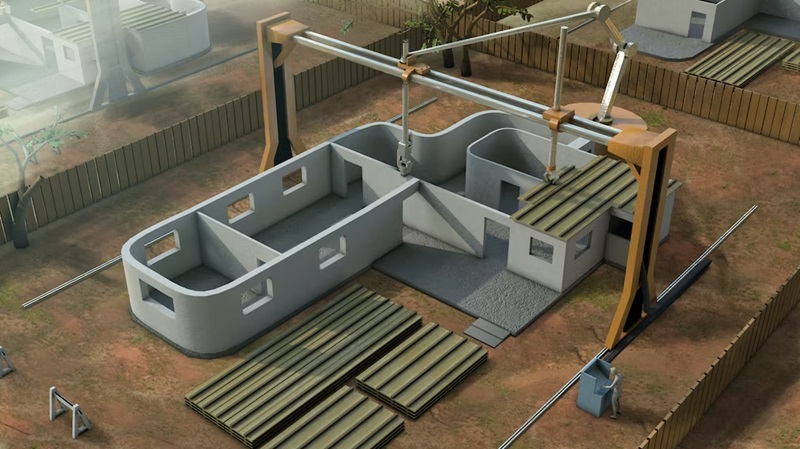
In recent years, the transformative impact of 3D printing has become increasingly evident across various industries, and the construction sector is no exception. This article delves into the profound innovations within 3D printing for construction, specifically focusing on the dynamic developments in both materials and techniques. As the construction landscape undergoes a paradigm shift, exploring these cutting-edge advancements becomes crucial for understanding the evolving dynamics of this revolutionary technology.
Robotic Arm Extrusion Techniques
In the dynamic landscape of construction, the transformative journey of 3D printing assumes a central role, with its evolution intricately woven into the fabric of technological progress. An indispensable facet of this revolution resides in the continuous refinement and enhancement of extrusion techniques, a domain where innovative strides are being made. Notably, the integration of robotic arms armed with state-of-the-art extrusion mechanisms emerges as a pivotal chapter in this narrative. These robotic arms, equipped with a symphony of technological intricacies, have redefined the very essence of construction methodology. Their ability to execute precise and controlled layering of diverse construction materials constitutes a groundbreaking achievement.
The Rise of Sustainable Materials
Within the realm of 3D printing for construction, there has been a discernible shift towards embracing sustainability through the integration of eco-friendly materials. Architects and engineers are actively exploring alternatives like recycled plastics, bio-based materials, and ideas like practical reinforced concrete modeling services that are able not only to reduce environmental impact but also to enhance the structural integrity and longevity of 3D-printed structures. This emphasis on sustainability reflects a broader industry trend towards responsible and eco-conscious construction practices.
Integration of Smart Technologies
The synergy between 3D printing and smart technologies is reshaping construction practices. The incorporation of sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) devices into the 3D printing process facilitates real-time monitoring of structural integrity. This not only ensures stringent quality control but also enables the timely identification of potential issues, heralding a new era of construction where technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing both efficiency and safety.
Customization and Design Flexibility
One of the hallmark advantages of 3D printing in construction lies in the unparalleled design flexibility and customization it affords. Architects now have the ability to push the boundaries of traditional design, creating structures that are not only functionally optimized but also exhibit unprecedented aesthetic uniqueness. This newfound freedom in design has transformative implications, unlocking the potential for architects to bring to life ambitious and innovative architectural visions.
Rapid Construction Speed
The remarkable speed of 3D printing in construction stands out as a game-changer. Traditional construction projects often span months or even years, but 3D printing technology has the potential to reduce construction timelines significantly. Entire structures can now be erected in a matter of days, presenting a paradigm shift in construction efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This rapid construction speed is poised to redefine industry standards and expectations.
Advancements in Printable Materials
The continuous expansion of materials compatible with 3D printing in construction showcases the ongoing advancements in the field. Beyond the conventional use of concrete and plastics, researchers are pushing the boundaries by exploring advanced composite materials. These materials offer heightened strength and durability, contributing to the creation of resilient structures capable of withstanding diverse environmental conditions. The evolving palette of printable materials is broadening the scope of possibilities within 3D-printed construction.
Large-Scale 3D Printing
A notable progression within 3D printing for construction is the shift from small-scale prototypes to large-scale projects. The capability to 3D print entire buildings on-site is indicative of the technology’s scalability. This evolution has profound implications for urban planning, as large-scale 3D printing opens avenues for more efficient use of space and resources. The ability to construct entire buildings through 3D printing marks a transformative leap towards reshaping urban landscapes.
Addressing Regulatory Challenges
The burgeoning adoption of 3D printing techniques is reshaping the industry’s trajectory. As this revolutionary technology gains increasing momentum, it brings to the forefront a complex array of regulatory challenges that demand careful consideration and strategic solutions. The imperative task at hand involves the standardization of codes and regulations specifically tailored to accommodate the unique aspects of 3D-printed structures. The ongoing collaborative efforts among various stakeholders within the construction and regulatory spheres underscore the commitment to establishing comprehensive guidelines. These guidelines are not merely a set of rules but a pivotal framework aimed at ensuring the safety, structural integrity, and overall compliance of structures constructed through innovative 3D printing methods.
In conclusion, the realm of 3D printing construction is witnessing a dynamic convergence of innovative materials and cutting-edge techniques. From sustainable practices to smart technologies, the industry is pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in construction. As the field continues to evolve, it holds the promise of reshaping how we build our world, offering solutions that are not only efficient but also environmentally conscious. The 3D printing revolution in construction is underway, and the future holds exciting possibilities for the built environment.